Japanese clock
(The late Edo Period)

Mechanism

Time table graph
おもしろ体験博物館
江戸民具街道の展示品紹介
Japanese Folk Art Museum
What you can see at Edo Mingu Kaido
Home >展示品紹介(Exhibits) >和時計(Japanese clock)
2.時の道具
Time keeping device
機械式和時計
Mechanical Japanese clock
江戸時代の日本では西洋の24時間定時法とは異なる不定時法と呼ばれる時刻制度が採用されていました。これは昼と夜をそれぞれ太陽の角度で六分割するというものです。太陽が真上に南天したところが九つ、そこから30度の角度毎に八つ、七つとなり日没が暮れ六つ、さらに五つ、四つと数えた後、太陽が真裏に位置したところから改めて九つ、八つ、七つと数え、日の出が明け六つとなり、五つ、四つで一巡します。昼間は太陽の角度が時計の文字盤替わりになるので大変便利であったと思われます。年間を通して日照時間の長さが変化するので季節毎に一刻の長さも変わりますが、当時の生活習慣においては十分であったものと思われます。
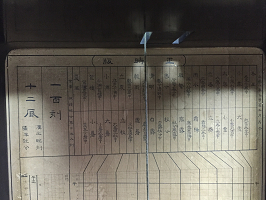
江戸時代には既に和時計が存在していましたがその構造は非常に複雑です。江戸民具街道で展示している和時計は加賀藩が19世紀前半に使っていたもので、重りが下がりながら時刻を示す尺時計と呼ばれる構造に似た大型の和時計です。時刻を読取る目盛盤には季節に応じた昼と夜の時刻が表示されており、振子とテンプの機構による一日の誤差は10秒以内で江戸末期の工作技術の高さを物語っています。加賀藩ではこの時計を基準時として時報代わりに時鐘を鳴らしていました。
明治5年(1872年)に西洋の24時間の定時法に移行した後、国産の西欧時間時計が生産されて始めますが、西洋時計の量産に対応できたのも江戸期に和時計の工作技術があったからだと思います。体験教室には明治、大正、昭和初期に作られた精巧舎や愛知時計等の振子時計のコレクションが展示されています。
During the Edo Period, the Japanese utilized the time keeping system called
Futejiho (varying length system) in which hours are defined by seasonally
changing sun 's celestial objects infestation being divided into 6 equal parts
(30 degrees each). During the day time, people could tell time by the
position of the sun and therefore, the system could have been convenient for the
people living in the era without clocks or watches. As the length of day
and night varies throughout the year, so were hours in this time keeping system,
which was totally different from western 24 hours system with each
hour being exactly 60mins.
There were clocks already existed during the Edo
Period and their mechanism and operation were very complicated to match
Futeijiho timing keeping system. The clock
exhibited at Edo Mingu Kaido is a large pillar type clock used at Kaga (current Kanazawa) feudal domain in the first half of the
19th century, a weight driven mechanical clock in which the poision of a weight
indicates time with a combination of a time table. In the time table graph
on its body that indicates the time, the day time and the night time for the 24
seasons of the year are precisely drawn. The clock has an error range of
less than 10 seconds per day and it is quite amazing to know that there was a
highly advance technology in Japan nearly 200 years ago. Kaga feudal
domain used the clock to keep standard time and rang bells to announce time.
In 1872, Japanese government introduced the western 24 hours timetable and
in the Meiji Period, the domestic clocks were started to be produced by
manufacturers such as Seiko. Thanks to the technologies developed during
the Edo Period, they were capable in mass-producing clocks domestically.
| 和時計 Japanese clock (The late Edo Period)  |
和時計機械部分 Mechanism  |
和時計文字盤 Time table graph  |
<<<Previous前の展示品ページ Next次の展示品ページ>>>
おもしろ体験博物館江戸民具街道
神奈川県足柄上群中井町久所418
0465-81-5339
Japanese Folk Art Museum "Edo Mingu Kaido"
Address: 418 Kuzo, Nakai-machi, Ashigara-kamigun, Kanagawa-ken, Japan
Tel: 0465-81-5339